Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toh, Yosuke; Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Huang, M.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Hideo
no journal, ,
Asai, Shiho; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Konda, Miki; Suzuki, Daisuke; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi
no journal, ,
Isotopes of Zr and Mo including both radio and stable isotopes can be found in spent nuclear fuel. Of these isotopes,  Zr and
Zr and  Mo which have long half-lives of 1.61
Mo which have long half-lives of 1.61  10
10 y and 4
y and 4  10
10 y, respectively, are of great importance from the viewpoint of managing high-level radioactive wastes in a long-term basis. In this study, contents of Zr and Mo isotopes in spent nuclear fuel solution were determined by isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The sample solution was prepared by dissolving a Japanese PWR irradiated UO
y, respectively, are of great importance from the viewpoint of managing high-level radioactive wastes in a long-term basis. In this study, contents of Zr and Mo isotopes in spent nuclear fuel solution were determined by isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The sample solution was prepared by dissolving a Japanese PWR irradiated UO fuel with a burnup of 51 GWd/t. The measured contents of
fuel with a burnup of 51 GWd/t. The measured contents of  Zr,
Zr, 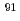 Zr,
Zr, 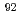 Zr,
Zr,  Zr,
Zr,  Zr, and
Zr, and 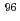 Zr in the sample were agreed well with the predicted values obtained through a burnup calculation code ORIGEN2. For Mo, the contents in the sample were approximately 30% less than the predicted values, indicating that part of Mo exists in the insoluble residue.
Zr in the sample were agreed well with the predicted values obtained through a burnup calculation code ORIGEN2. For Mo, the contents in the sample were approximately 30% less than the predicted values, indicating that part of Mo exists in the insoluble residue.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc separation-concentration apparatus based on solvent extraction and column chromatography
Tc separation-concentration apparatus based on solvent extraction and column chromatographyTsuchiya, Kunihiko; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Nishikata, Kaori; Shibata, Akira; Nakamura, Natsuki; Tanase, Masakazu*; Shiina, Takayuki*; Ota, Akio*; Kawabata, Masako*; Takeuchi, Nobuhiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagame, Yuichiro
no journal, ,
Tsukada, Kazuaki; Watanabe, Satoshi*; Ishioka, Noriko*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Sugo, Yumi*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kin, Tadahiro*; Kawabata, Masako*; Saeki, Hideya*; et al.
no journal, ,
A new system has been proposed for the generation of radioisotopes with accelerator neutrons by deuterons, especially the production of Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64. Enriched Mo-100, Zr-90, Zn-68 and Zn-64 oxide samples were irradiated with neutrons, which were obtained by the  C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 12 - 50 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron and the JAEA tandem accelerator. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the
C(d,n) and Be(d,n) using 12 - 50 MeV deuterons provided from the TIARA cyclotron and the JAEA tandem accelerator. Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64 were successfully produced via the (n, x) reactions, and we clearly observed the  -rays. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
-rays. The present results demonstrate that the radioisotopes, Mo-99, Y-90, Cu-67, and Cu-64, can be produced by using fast neutrons, and strongly suggest that the reaction system is one of the most promising routes to produce high quality medical radioisotope.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina*; Takeda, Shinsaku*; Vascon, A.*; Sakama, Minoru*; Sato, Daisuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.